Eelgrass (Zostera marina) beds
Classification
Description
GB distribution
Compiled by: Keith Hiscock, English Nature, Northminster House, Peterborough PE1 1UA.
UK.
Derived, in part, from: the UK marine biotope classification (Connor et al.
1997b) and a review undertaken for the UK Marine SACs Project (Davison 1998).
Classification
| Classification |
Code |
Biotope(s) |
| Europe (EUNIS Nov. 1999) |
A4.5/B-IMS.Sgr.Zmar |
Zostera beds in lower shore or infralittoral clean or
muddy sand. |
| Wadden Sea |
03.02.05 |
Benthic zone of the shallow coastal waters with muddy and
sandy bottom, rich in macrophytes |
| Britain/Ireland (MNCR BioMar 97.06) |
IMS.Zmar |
Zostera marina/angustifolia beds in lower shore
or infralittoral clean or muddy sand |
| France (ZNIEFF-MER) |
II.3.3 III.3.4 |
Herbiers de Zostera marina, Zostera noltii (= Z.
nana pro parte) du médiolittoral inférieur Herbiers de Zostera marina |
Description
IMS.Zmar. Expanses of clean or muddy fine sand in shallow water and on the lower shore
(typically to about 5 m depth) can have dense stands of Zostera marina/angustifolia
[Note: the taxonomic status of Z. angustifolia is currently under consideration but
is most likely a dwarf form of Zostera marina]. In IMS.Zmar the community
composition may be dominated by these Zostera species and therefore characterised
by the associated biota. Other biota present can be closely related to that of areas of
sediment not containing Zostera marina, for example, Laminaria saccharina, Chorda
filum and infaunal species such as Ensis spp. and Echinocardium cordatum
(e.g. Bamber 1993) and other bivalves listed below. It should be noted that sparse beds of
Zostera marina might be more readily characterised by their infaunal community.
Beds of this biotope in south-west Britain may contain conspicuous and distinctive
assemblages of Lusitanian fauna such as Laomedea angulata, Hippocampus spp.
and Stauromedusae. Some examples of Zostera marina beds have markedly anoxic
sediments associated with them.
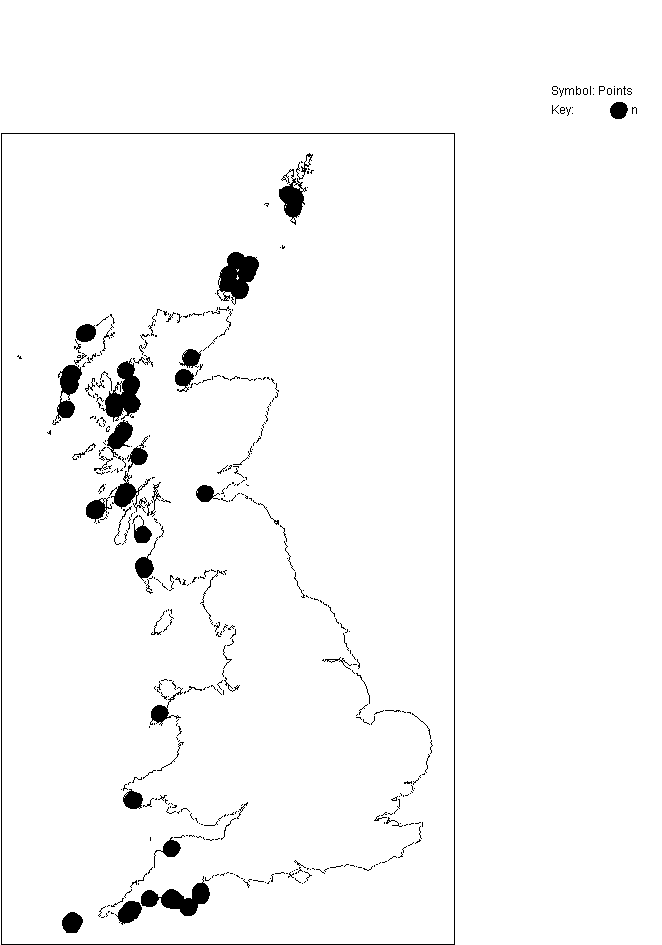
GB distribution (from MNCR database March 1999)
Habitat requirements
Species composition and biodiversity
Ecological relationships
Sensitivity to human activities
Conservation and protection status
References
|

