Exposed infralittoral rock with kelp
Classification
Description
GB distribution
Compiled by: Leigh Jones, Joint Nature Conservation Committee, Monkstone House, City
Road, Peterborough PE1 IJY, UK.
Derived, in part, from: the UK marine biotope classification (Connor et al.
1997b) and a review undertaken for the UK Marine SACs Project (Birkett et al.1998).
Classification
| Classification |
Code |
Biotope(s) |
| Europe (EUNIS Nov. 1999) |
A3.1 |
Infralittoral rock very exposed to wave action and/or
currents and tidal streams. |
| Wadden Sea |
- |
Not present |
| Britain/Ireland (MNCR BioMar 97.06) |
EIR.KFaR |
Kelp with cushion fauna, foliose red seweeds or coralline
crusts (exposed rock) |
| France (ZNIEFF-MER) |
III.9.3.3 |
Faciès à Laminaria hyperborea-Laminaria ochroleuca:
sous-faciès à L. hyperborea en population pure (eau claire, mode battu à très
battu) |
Description
Rocky habitats in the infralittoral zone subject to exposed to extremely exposed wave
action or strong tidal streams. Typically the rock supports a community of kelp Laminaria
hyperborea with foliose seaweeds and animals, the latter tending to become more
prominent in areas of stongest water movement. The depth to which the kelp extends varies
according to water clarity, exceptionally (e.g. St Kilda) reaching 45 m. The sublittoral
fringe is characterised by dabberlocks Alaria esculenta, or occasionally by the
kelp Saccorhiza polysichides. In very strong wave action the sublittoral fringe Alaria
zone extends to 5 to 10 m, whilst at Rockall Alaria replaces L. hyperborea
as the dominant kelp in the infralittoral. In some areas, there may be a band of dense
foliose seaweeds (reds or browns) below the main kelp zone.
(see also habitat reviews for moderately exposed infralittoral kelp and sheltered
infralittoral kelp.)
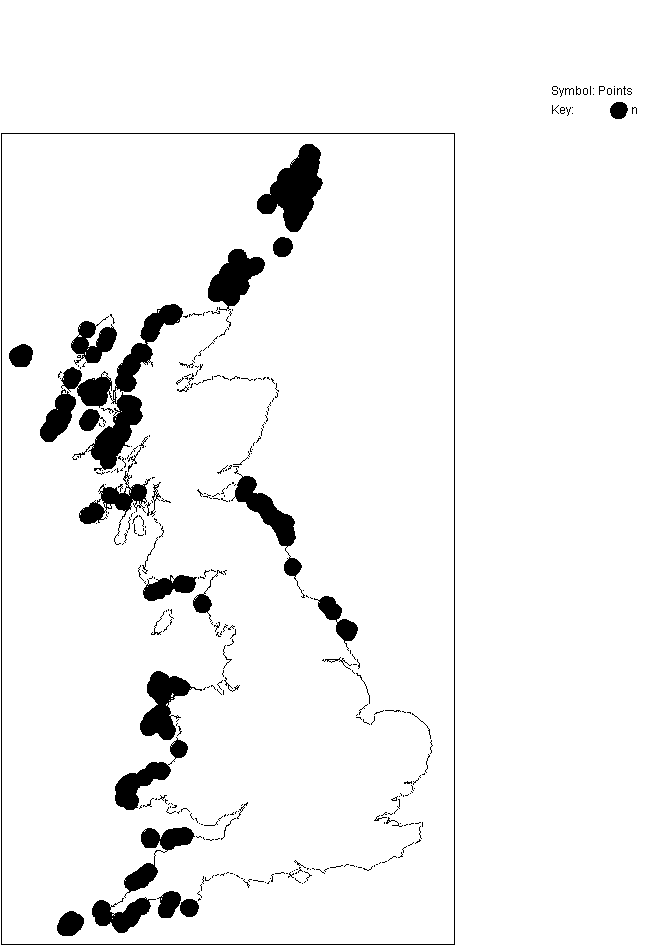
GB distribution
(from MNCR database in February 1999)
Habitat requirements
Species composition and biodiversity
Ecological relationships
Sensitivity to human activities
Conservation and protection status
References
|

