Eelgrass (Zostera noltii) beds
Classification
Description
GB distribution
Compiled by: Leigh Jones, Joint Nature Conservation Committee, Monkstone House, City
Road, Peterborough PE1 IJY, UK.
Derived, in part, from: the UK marine biotope classification (Connor et al.
1997a) and a review undertaken for the UK Marine SACs Project (Davison 1998).
Classification
| Classification |
Code |
Biotope(s) |
| Europe (EUNIS Nov. 1999) |
A2.71/B-LMS.Zos.Znol |
Zostera noltii beds in upper to mid shore muddy sand |
| Wadden Sea |
05.02.01 |
Intertidal seagrass beds |
| Britain/Ireland (MNCR BioMar 97.06) |
LMS.Znol |
Zostera noltii beds in upper to mid shore muddy sand |
| France (ZNIEFF-MER) |
II.3.3
III.3.7 |
Herbiers de Zostera marina, Zostera noltii (= Z.
nana pro parte) du médiolittoral inférieur Biocenose des sables vaseux
superficiels de mode calme (SVMC) |
Description
Mid and upper shore wave-sheltered muddy fine sand or sandy mud with narrow-leafed eel
grass Zostera noltii at an abundance of frequent or above. This is similar to
polychaetes and Cerastoderma edule (LMS.PCer) since it is most frequently found on
lower estuary and sheltered coastal muddy sands with a similar infauna. Exactly what
determines the distribution of the Zostera noltii is, however, not entirely clear. Zostera
noltii is often found in small lagoons and pools, remaining permanently submerged, and
on sediment shores where the muddiness of the sediment retains water and stops the roots
from drying out. A black layer is usually present below 5 cm sediment depth. The infaunal
community is characterised by polychaetes Pygospio elegans and Arenicola marina,
mud amphipods Corophium volutator and bivalves Cerastoderma edule, Macoma
balthica and Scrobicularia plana. Typically an epifaunal community is found
that includes the mud snail Hydrobia ulvae, shore crabs Carcinus maenas and
the green alga Enteromorpha sp. This biotope should not be confused with IMS.Zmar,
which is a Zostera marina bed on the lower shore or shallow sublittoral clean or
muddy sand.
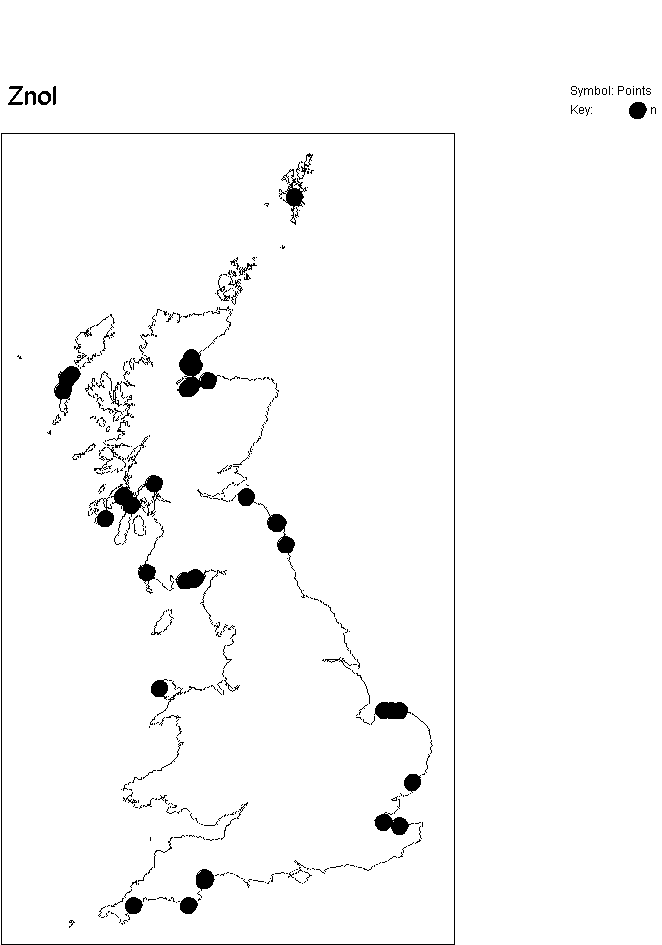
GB distribution
(from MNCR database in February 1999)
Habitat requirements
Species composition and biodiversity
Ecological relationships
Sensitivity to human activities
Conservation and protection status
References
|

